Modern Parking Management Systems: How to Choose the Right Barrier Gate Type
In today’s fast-growing urban environments, efficient parking management is essential. Whether for shopping centers, office buildings, residential complexes, or public facilities, selecting the right barrier gate is a critical decision. The right gate not only improves security and user experience but also ensures reliability and low maintenance over time. This guide will walk you through the various types of barrier gates, key factors to consider, and how to match gate types with your specific usage needs.

What Is a Barrier Gate?
A barrier gate (sometimes called a boom gate or swing arm gate) is a mechanical system that controls vehicular access by raising and lowering an arm (boom) or operating a retractable barrier. Barrier gates are typically integrated into parking management systems, access control systems, or security perimeters. They help in restricting unauthorized entry, facilitating payment or permit-based access, managing traffic flow, and enhancing safety.
Common Types of Barrier Gates
Here are the main kinds of barrier gates you’ll find, their advantages, and ideal usage scenarios.
| Barrier Gate Type | How It Operates | Pros | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Barrier/Arm Gates | Operated by a guard or attendant, either manually lifting the arm or via simple lever mechanism. | Low cost, simple installation, minimal maintenance. | Small parking lots, gated communities, temporary events. |
| Electro-Mechanical Boom Gates | Powered by motor & gearbox; may include spring or counterweight assist. Hinge point raises and lowers the arm. | Moderate speed, reliable operation, suited for frequent use. | Commercial parking lots, apartment complexes. |
| Hydraulic Boom Gates | Use hydraulic rams/motors for smooth operation, especially for long or heavy arms. | Very durable, smooth motion, less vibration, good for heavy-duty tasks. | High-traffic entrances, wide lanes, industrial settings. |
| Telescopic Boom Gates | Boom consists of retractable sections that slide into each other. | Saves horizontal space when the arm retracts; faster operation; good for wide lanes. | Airports, wide vehicle lanes, tight sites where opening space is limited. |
| Swing/Gate Barrier Systems | Instead of a boom, uses a full gate panel (swing gate) that opens like a door. | Complete barrier, higher security, robust presence. | High security zones, entry points required to block entire opening. |
| Folding Arm Barrier Gates | Barrier arm folds in one or more joints rather than swinging or straight lifting. | Conserves space, faster movement, reduced clearance required. | Sites with height restrictions, narrow entrance zones. |
| Smart/Automatic Barrier Systems | Includes features like license plate recognition (LPR), RFID, remote control, app integration, payment kiosks. | Enhanced convenience and security, can automate many functions. | Malls, urban parking garages, secure facilities. |
Key Criteria for Selecting the Right Barrier Gate
Choosing the right barrier gate involves evaluating several factors. Here are the most important ones:
1. Traffic Volume & Frequency
- Low vs High Frequency: If you expect many cars per hour (e.g. commercial or public parking), you need a durable, fast-acting model (electro-mechanical or hydraulic).
- Peak Loads: Consider morning/evening rush, special events, or full parking turnover periods.
2. Lane Width & Boom Length
- Long booms (to cover wide lanes) place more stress on the mechanism; you’ll need stronger motors or hydraulic systems.
- Telescopic booms or folding arms can help with very wide lanes without requiring very large swing clearance.
3. Speed & Response Time
- Frequent usage demands gates that open/close quickly (2-5 seconds for boom operation might be acceptable in many contexts).
- You should balance speed with safety—faster movement must still allow safe stopping and presence detection to avoid accidents.
4. Durability & Weather Resistance
- Material choice and finishing matter: anti-corrosion coatings, stainless components, sealed motors.
- In harsh climates (rain, salt air, snow, extreme heat), select gates rated for those conditions and ensure protective elements (e.g. waterproof housing, rugged construction).
5. Safety Features
- Presence detection (photoelectric sensors, loop detectors).
- Emergency manual release in case of power failure.
- Soft start / soft stop to reduce mechanical shock.
- Optional safety edges to avoid pinching or damaging vehicles/pedestrians.
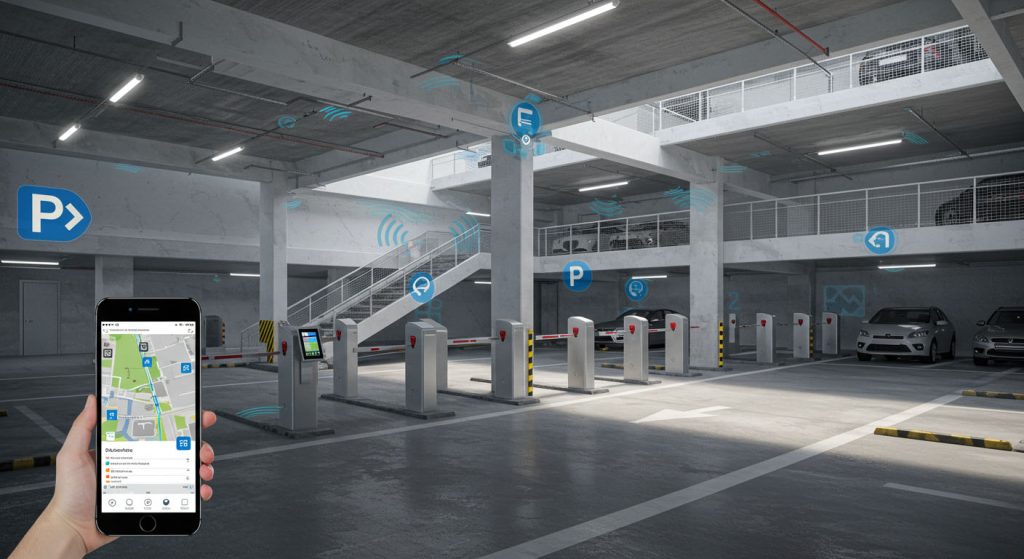
6. Integration with Access & Payment Systems
- RFID cards or tags, barcode or QR code readers, ticket dispensers, license plate recognition.
- Remote control or mobile app integration.
- Central monitoring: data logging, remote diagnostics, usage stats.
7. Maintenance Requirements & Lifecycle Costs
- Components subject to wear: motors, springs, hydraulic oil, boom arm hinges.
- Cost of spare parts and routine service.
- Ease of servicing: accessibility of moving parts, ability to replace components without dismantling major assemblies.
8. Aesthetic & Regulatory Considerations
- Appearance: design, color, branding opportunities, visibility (reflectors, lights).
- Compliance with local building codes, safety regulations, barrier height or width restrictions.
- Noise level: quieter systems will be desired in residential or mixed zones.
Matching Gate Types to Specific Scenarios
Here are several typical scenarios and which gate types tend to work best in those contexts:
| Scenario | Ideal Barrier Gate Type(s) | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Small neighborhood with < 20 cars/hr | Manual or basic electro-mechanical boom gates | Lower cost, less demand, simple systems are adequate. |
| Large retail shopping mall | Electro-mechanical booms or telescopic booms, plus smart control | High throughput, peak demand, need fast, reliable and automated access control. |
| Industrial site or truck entrance | Heavy-duty hydraulic boom gates or full swing gates | Need to handle large, heavy vehicles; long booms; durability. |
| Airport or stadium | Telescopic booms, folding arms, and license plate recognition systems | Wide lanes, tight scheduling, high throughput, advanced automation. |
| Residential high-rise or apartment complex | Electro-mechanical boom with RFID or barrier arm with remote access | Balance security, aesthetics, and cost; less heavy duty but more convenience. |
| Parking garages with ceiling height restrictions | Folding arms or telescopic gates | Avoid interference with overhead constraints; maximize space. |
Cost Considerations
Budgeting properly for a barrier gate involves more than just the purchase price. Here’s what you should factor in:
- Initial purchase & installation: Includes gate cost, civil works (foundations, lane pavement), electrical supply. Telescopic or hydraulic systems cost more initially.
- Operational costs: Power consumption, control system (software licensing, if any), energy for frequent actuation.
- Maintenance & spare parts: Hinges, motor brushes, hydraulic seals.
- Downtime costs: A faulty gate at a busy entrance causes delays, security risk, and may create liability issues.
Best Practices for Implementation
To get the most value out of your barrier gate, follow these best practices:
- Use Site Surveys
Before purchase, have a professional site survey to assess space, lane width, traffic patterns, power availability, and environmental conditions. - Standardize Components
If you manage multiple sites, standardizing brands or gate models simplifies maintenance and spare parts inventories. - Ensure Proper Foundation & Install
Even the best mechanical gate will fail prematurely if the base is weak or unlevel. Concrete mounting pads, correct alignment, and solid supports are crucial. - Test Safety and Compliance
Make sure all sensors, emergency releases, and fail-safe modes function properly. Document testing for compliance. - Plan for Power Failures / Backup
Include manual override or battery backup so gates can open safely during outages. - Monitor and Maintain Regularly
Schedule regular inspection, lubrication, cleaning. Track usage to anticipate wear and replace parts before they fail.
Trends in Barrier Gate Technology
The parking management industry is evolving fast. Some trends to watch:
- Automated License Plate Recognition (LPR) for hands-free entry.
- IoT-connected gates, sending diagnostics, usage stats, and alerts remotely.
- Solar-powered barrier gates in off-grid or remote locations.
- Fast-acting gates with faster open/close cycles to improve traffic throughput.
- Integrated Payment Solutions embedded in gates or connected via apps for cashless parking.
Conclusion
Barrier gates are more than just a physical arm across a driveway; they are an essential component in modern parking management that influences security, efficiency, user satisfaction, and maintenance costs. To choose the ideal barrier gate, consider factors like traffic volume, lane width, speed, durability, safety, integration with access systems, and total cost of ownership.


 FACEBOOK
FACEBOOK
 TWITTER
TWITTER
 LINKEDIN
LINKEDIN